top of page

POSTER SESSION
Click the icons below to learn more about our presenters, poster abstracts, and access links to their research groups.
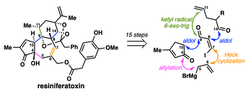
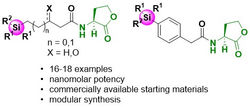
Organic Synthesis
Chemical Biology & Bioinorganic
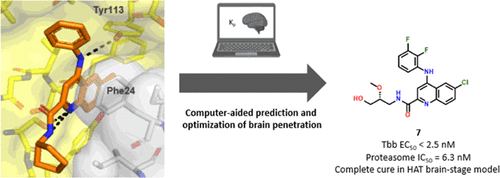
Medicinal & Computational Chemistry
EWOC
bottom of page